EXPERIMENT- 4 Anderson’s Bridge
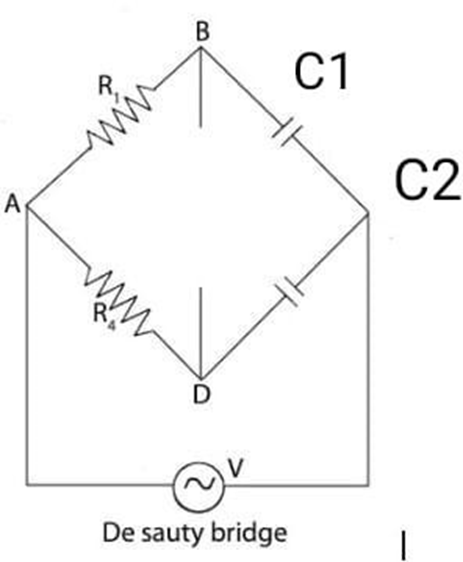
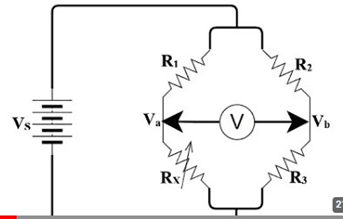
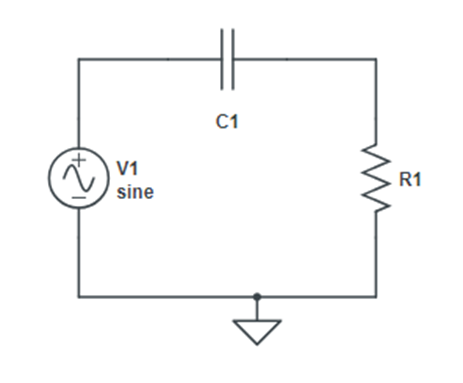
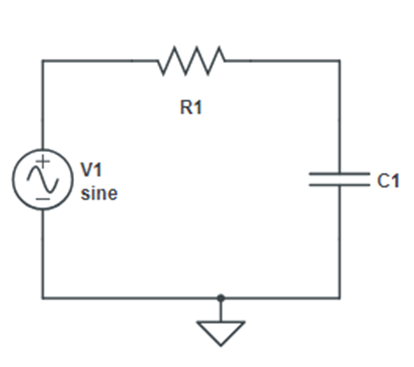
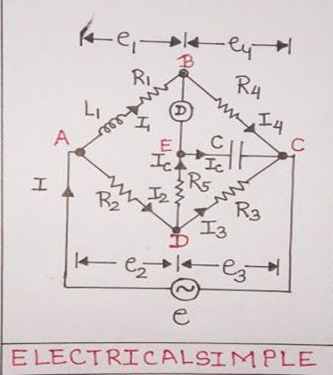
Aim– Measurement of Inductance by Anderson’s Bridge. Material Required– Anderson Bridge Trainer Kit, Wires Theory– The Anderson bridge is a bridge circuit used for measuring unknown resistances, especially those with high values. The bridge is balanced when the ratio of the resistances in the adjacent arms is equal. Circuit Diagram- Formula used and derivation – […]
EXPERIMENT- 4 Anderson’s Bridge Read More »
BASIC INSTRUMENTAION AND MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES