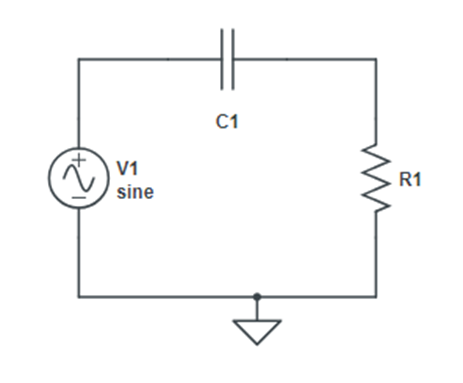
Experiment 10 High Pass Filter
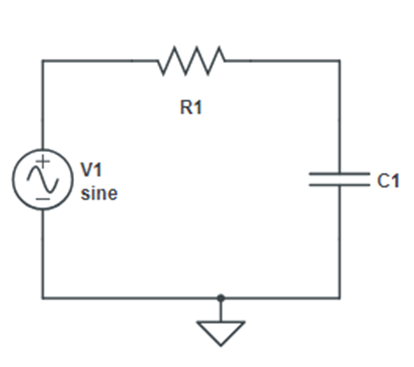
Aim: To design RC high pass filter and study its frequency response Apparatus Required: Theory: A filter is a circuit that passes a specific range of frequencies while rejecting other frequencies. A passive filter consists of passive circuit element such as capacitor, inductor and resistor. A highpass filter is formed when the output of an […]
Experiment 10 High Pass Filter Read More »
BASIC CIRCUIT THEORY, BASIC CIRCUIT THEORY, SEM 1