Experiment 8
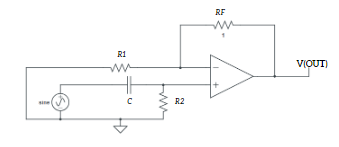
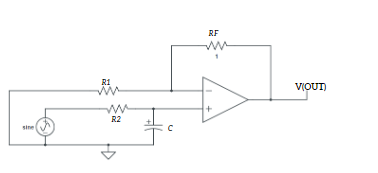
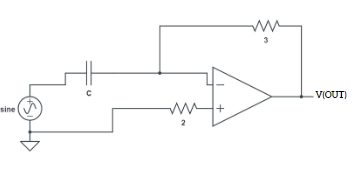
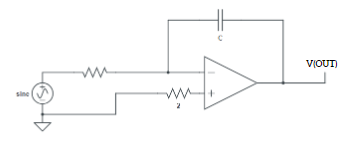
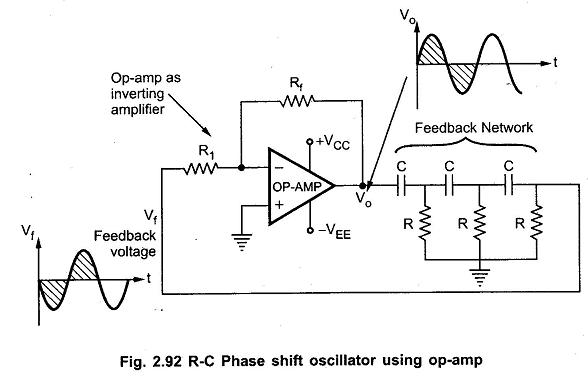
Aim: Designing a RC phase shift oscillator using op amp.Apparatus Required: 741 IC, Multimeter, CRO, Dual power supply (15-0-15 V), Resistors, Capacitor, and connecting wires.Theory: A RC phase shift oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator circuit that generates sinusoidal signals. It utilises a network of resistors and capacitors (RC network) in a feedback loop […]