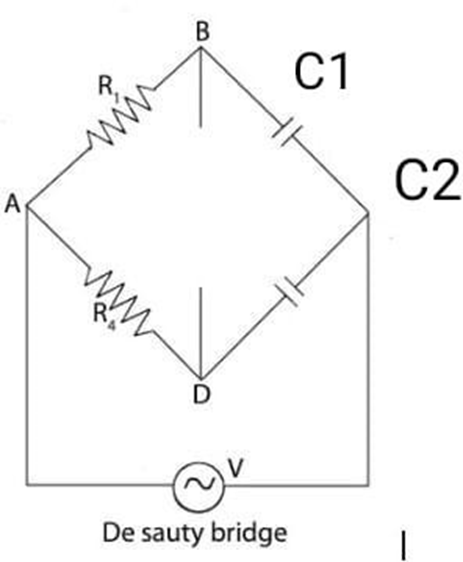
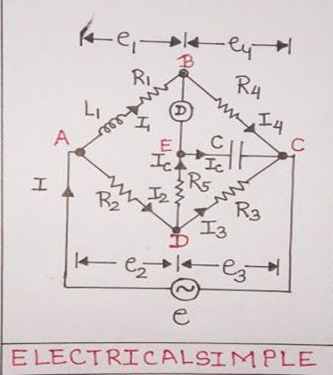
Aim- Measurement of Resistance by Wheatstone Bridge.
Apparatus- Galvanometer (0-10V), Decade Resistance Box, Resistance (4), Bread Board, Power Supply
Theory- The Wheatstone bridge works on the principle of null deflection, i.e. the ratio of their resistance is equal, and no current flows through the circuit. When the bridge is balanced,
the galvanometer reads zero. This occurs when the ratio of the resistances in the arms of the bridge satisfies the equation:
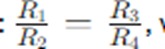
where R1, R2, R3, and R4 are the resistances in the respective arms.
Derivation-

Circuit Diagram-
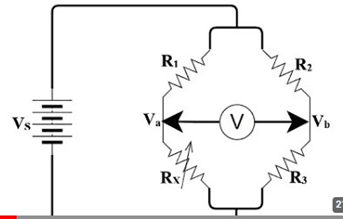
Procedure-
- Connect the circuit as per the diagram.
- Fix a particular value of R1 and R2.
- Vary the Decade Resistance Box to find the appropriate value of unknown resistor Rx till the galvanometer shows zero deflection or null deflection.
- Note down the value of resistance read by the resistance box using a multimeter.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 for different values of Rx.
Observation Table-
| Rx | RDB | Multimeter RDB | Actual value of Rx |
Result- The ratio of resistance is equal, and thus, the Wheatstone Bridge is verified.
Precautions-
- Make sure the connections are done properly.
- Calculate the values at the same voltage for the whole experiment.