Aim:
Verification of Superposition Theorem
Components and Equipment Required:
DC voltage source, resistance, ammeter, connecting wires, bread board
Theory:
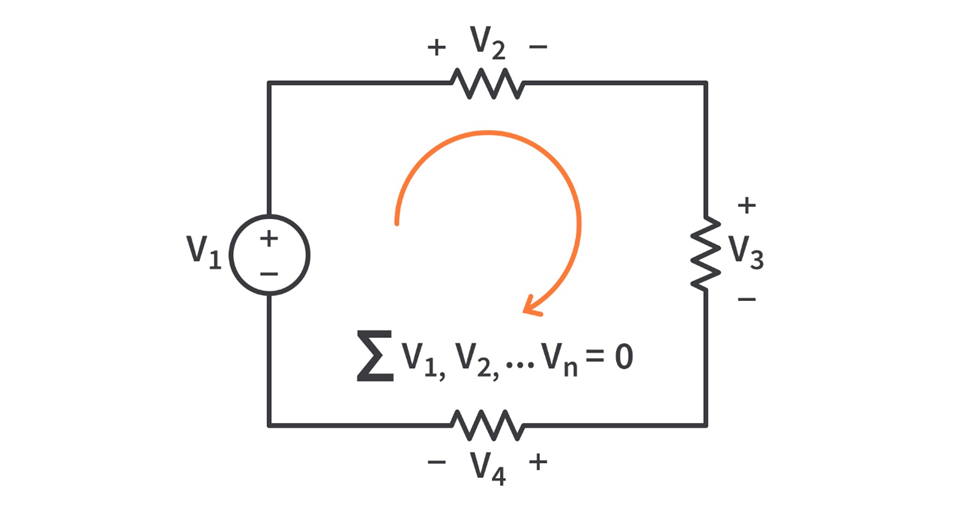
The superposition principle states that the voltage across (or current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone.
Stated differently, it facilitates the determination of solutions for individual currents or voltages generated by each source in isolation. Subsequently, upon obtaining the separate solutions for each source, combining the results enables us to determine the overall solution.
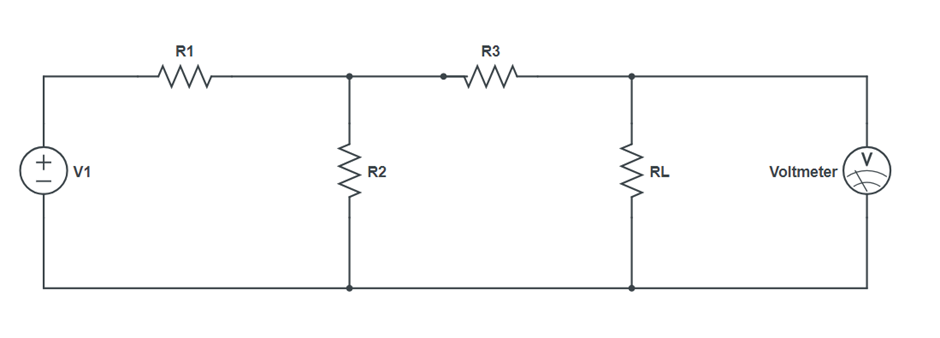
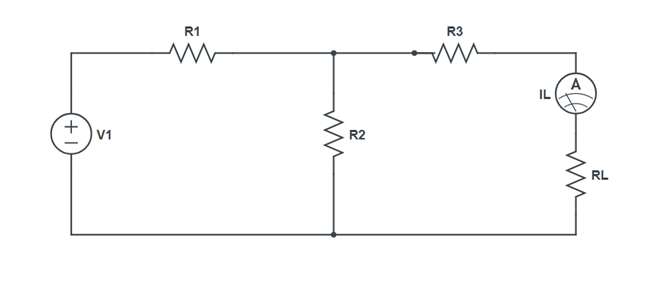
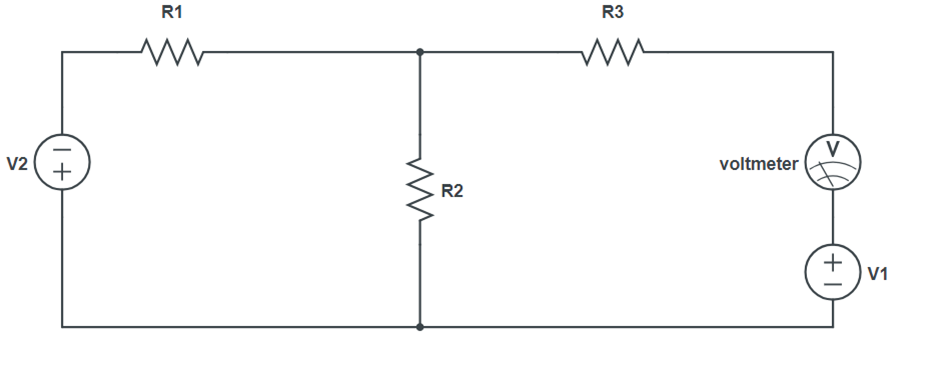
Circuit Diagram:
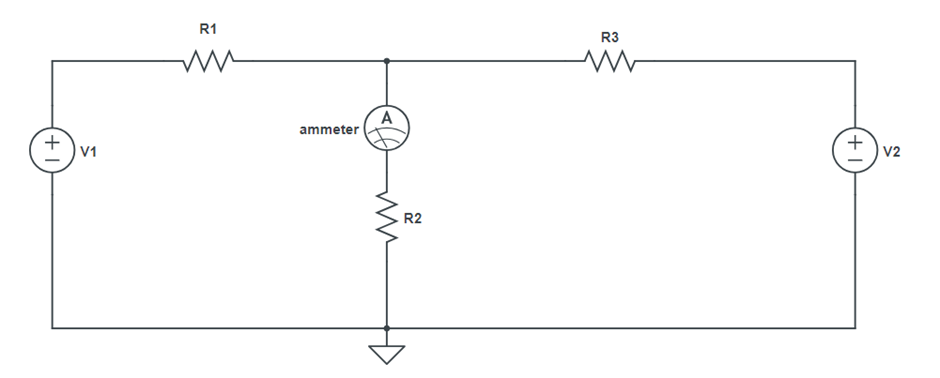
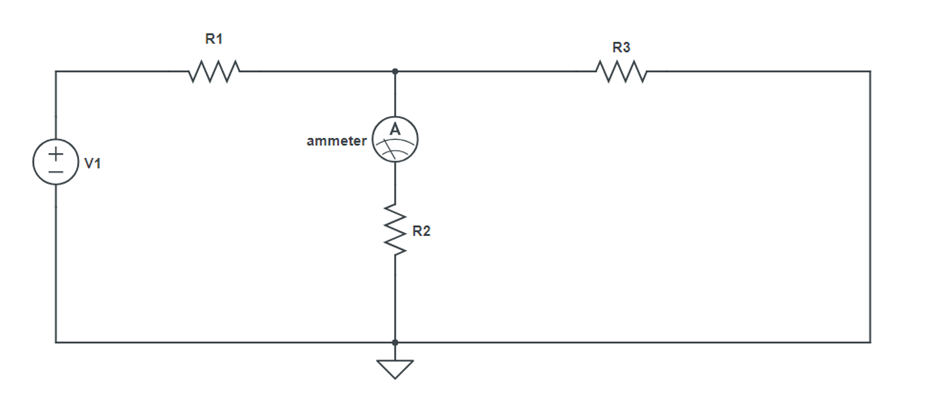
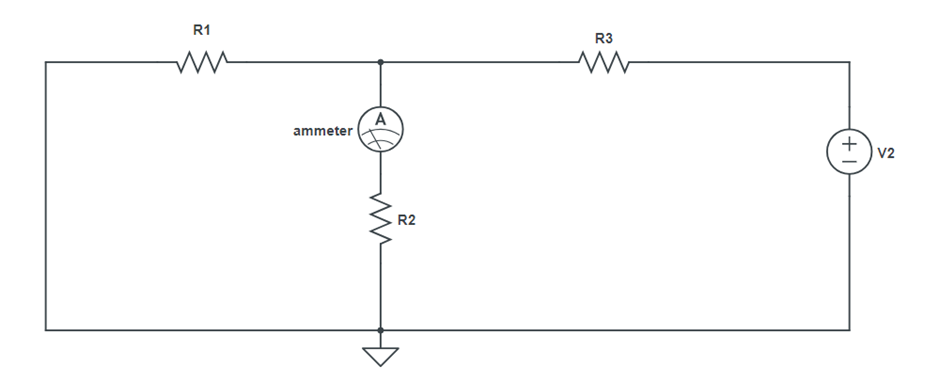
Procedure:
- Make the connections as per the diagram.
- Set a particular voltage value V1 and V2 & note down the ammeter reading (Figure 1)
- Set the same voltage in circuit 1 using V1 alone and short circuit the other terminals, note the ammeter reading. (Figure 2)
- Set the same voltage in V2 alone as in circuit 1 and note down the ammeter reading.
(Figure 3)
- Verify superposition theorem.
Observation Table:
| Current obtained | Theoretical values | Practical Values |
| V1, V2 both connected | ||
| V1 connected | ||
| V2 connected |
Result:
Thus, the Superposition Theorem is verified.
Precautions:
- Voltage control knob should be kept at minimum position
- Check if power supply and ammeter are working properly.