AIM: To study the I-V Characteristics of Ordinary Diode.
APPARATUS:
P-N Junction Diode, Battery, Connecting Wires, Resistances, Voltmeter, Ammeter.
THEORY:
A P-N junction is formed by doping the P-type with trivalent impurities which has excess holes and the N-type with pentavalent impurities which has excess electrons. In forward bias, a positive voltage on P allows current flow by reducing the potential barrier. In reverse bias, a negative voltage on P blocks current, creating a wider depletion region. The junction’s behavior depends on the type of impurities and bias applied. In step up, there is a reduction in potential barrier
In a PN junction diode, the positive and negative terminals are identified based on the p-type and n-type materials, respectively.
Cathode and Anode:
- The anode is the positive terminal and is connected to the p-type semiconductor.
- The cathode is the negative terminal and is connected to the n-type semiconductor.
- Most diodes have a band or line marking on the cathode end. This line, usually silver or white, distinguishes the negative side of the diode.
- The end without the line is the anode (positive) end.
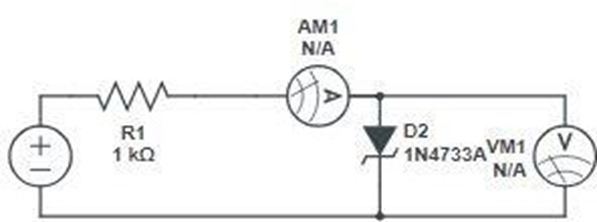
CIRCUITS:
Forward Bias:
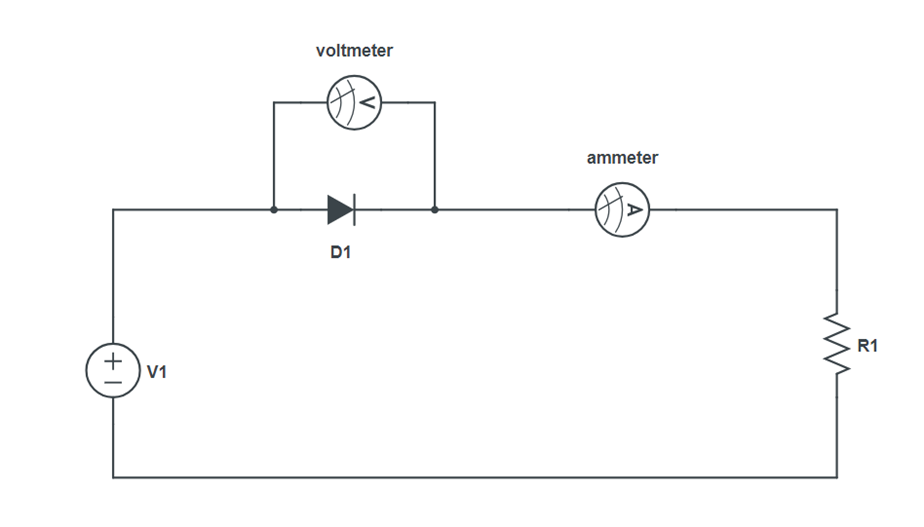
Reverse Bias:
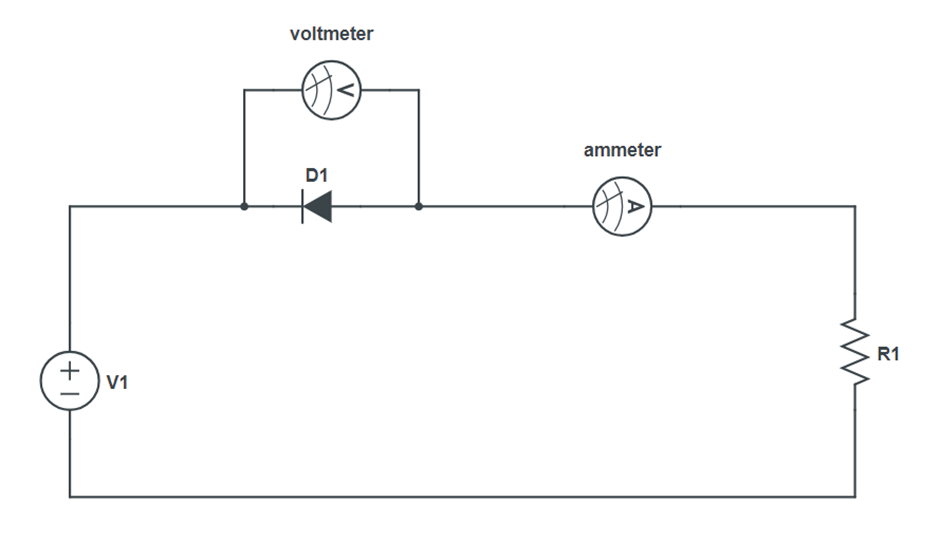
Graph:
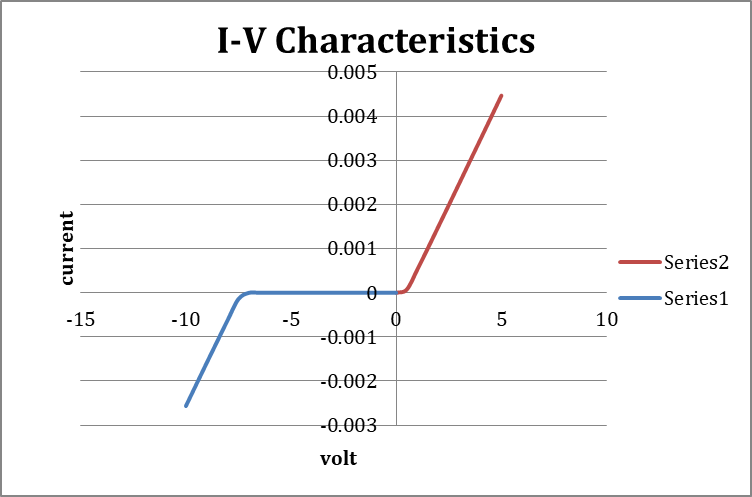
RESULT:
The V-I Characteristic Graphs/Curves of P-N Junction Diodes (both in reverse and forward biases) are obtained and are verified with their proven results.